The human skeleton of an adult consists of 206 bones. It is composed of 300 bones at birth, but later decreases to 80 bones in the axial skeleton and 126 bones in the appendicular skeleton. Many small supernumerary bones, such as some sesamoid bones, are not included in this count.
Introduction
Types of Bones in the Human Skeleton - Human Anatomy |Â Kenhub - Find more videos at: https://www.kenhub.com Subscribe to our YouTube channel: http://bit.ly/VOEG2I In this tutorial we will explore the different types of bones ...
As a human ages, some of its bones fuse, a process which typically lasts until sometime within the third decade of life. Therefore, the number of bones in an individual may be evaluated differently throughout their life. In addition, the bones of the skull and face are counted as separate bones, despite being fused naturally. Some reliable sesamoid bones such as the pisiform are counted, while others, such as the hallux sesamoids, are not.
Individuals may have more or fewer bones than the average (even accounting for developmental stage) owing to anatomical variations. The most common variations include sutural (wormian) bones, which are located along the sutural lines on the back of the skull, and sesamoid bones which develop within some tendons, mainly in the hands and feet. Some individuals may also have additional (i.e., supernumerary) cervical ribs or lumbar vertebrae.
Bones
Spine (vertebral column)
A fully grown adult features 26 bones in the spine, whereas a child can have 34.
- Cervical vertebrae (set of 7 bones)
- Thoracic vertebrae (set of 12 bones)
- Lumbar vertebrae (set of 5 bones)
- Sacral vertebrae (set of 5 bones at birth, and later fused into one)
- Coccygeal vertebrae (set of 5 bones at birth; some or all fuse together, but there seems to be a disagreement between researchers as to what the most common number should be. Some say the most common is 1, others say 2 or 3, with 4 being the least likely. It is counted as 1 in this article.)
Chest (thorax)
There are usually 25 bones in the chest but sometimes there can be additional cervical ribs in humans. Cervical ribs occur naturally in other animals such as reptiles.
- Sternum
- Ribs (24, in 12 pairs)
- It is important to note that three pairs (the 8th, 9th and 10th), also known as false ribs, are attached to each other. They are also attached to the 7th rib by cartilage and synovial joints. Also two pairs of floating ribs (the 11th and 12th), have no anterior attachment.
- Cervical ribs are extra ribs that occur in some humans.
Skull (cranium and mandible)
There are 22 bones in the skull. Including the hyoid and the bones of the middle ear, the head contains 29 bones.
- Cranial bones (8)
- Occipital bone
- Parietal bones (2)
- Frontal bone
- Temporal bones (2)
- Sphenoid bone (sometimes counted as facial)
- Ethmoid bone (sometimes counted as facial)
- Facial bones (14)
- Nasal bones (2)
- Maxillae (upper jaw) (2)
- Lacrimal bone (2)
- Zygomatic bone (2)
- Palatine bone (2)
- Inferior nasal concha (2)
- Vomer
- Mandible (lower jaw)
- Hyoid bone (not connected to any other bone)
- Middle ears (6)
- Malleus (2)
- Incus (2)
- Stapes (2)
Arm
There are a total of 64 bones in the arm.
- Upper arm bones (6 bones in total; 3 on each side)
- Humerus
- Pectoral girdle (shoulder)
- Scapula
- Clavicles
- Lower arm bones (4 bones, 2 on each side)
- Ulna
- Radius
- Hand (54 bones in total; 27 in each hand)
- Carpals
- Scaphoid bone (2)
- Lunate bone (2)
- Triquetral bone (2)
- Pisiform bone (2)
- Trapezium (2)
- Trapezoid bone (2)
- Capitate bone (2)
- Hamate bone (2)
- Metacarpals (10 bones in total; 5 in each side)
- Phalanges of the hand
- Proximal phalanges (10 bones in total; 5 in each side)
- Intermediate phalanges (8 bones in total; 4 in each side)
- Distal phalanges (10 bones in total; 5 in each side)
- Carpals
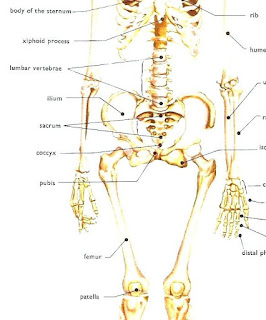
Pelvis (pelvic girdle)
The hip bone has three regions: ilium, ischium, and pubis (2)
- The sacrum and the coccyx attach to the two hip bones to form the pelvis, but are more important to the spinal column. For this reason it is omitted from the pelvic girdle.
Leg
- Femur (2)
- Patella or kneecap (2)
- Tibia (2)
- Fibula (2)
- Foot (52 bones in total, 26 per foot)
- Tarsus
- Calcaneus or heel bone (2)
- Talus (2)
- Navicular bone (2)
- Medial cuneiform bone (2)
- Intermediate cuneiform bone (2)
- Lateral cuneiform bone (2)
- Cuboid bone (2)
- Metatarsals (10)
- Phalanges of the foot
- Proximal phalanges (5 × 2 = 10)
- Intermediate phalanges (4 x 2 = 8)
- Distal phalanges (5 x 2 = 10)
- Tarsus
Sum
Spine 26 Chest 25 Head 29 Arms 64 Legs 60 Pelvis 2
(206)
Sesamoid bones
- Patella
- Pisiform bone
- Fabella
- Sesamoids in the first and second metacarpal bones
- Sesamoids in the first metatarsal bone
- Lenticular process of the incus
References
- The 206 Bones of the Human Body